Shreenath K.S.
Associate Program Head - Data Science
Author Bio:
Shreenath K.S. is an alumnus of Indian School of Business (ISB). He is currently the Associate Program Head - Data Science, eClerx Service Pvt Ltd. India. With 14+ years of professional experience, he is a Data Science mentor and advocate. He has worked in companies such as HP, Future Group, and TheMathCompany.
There is an enormous amount of data collected worldwide.
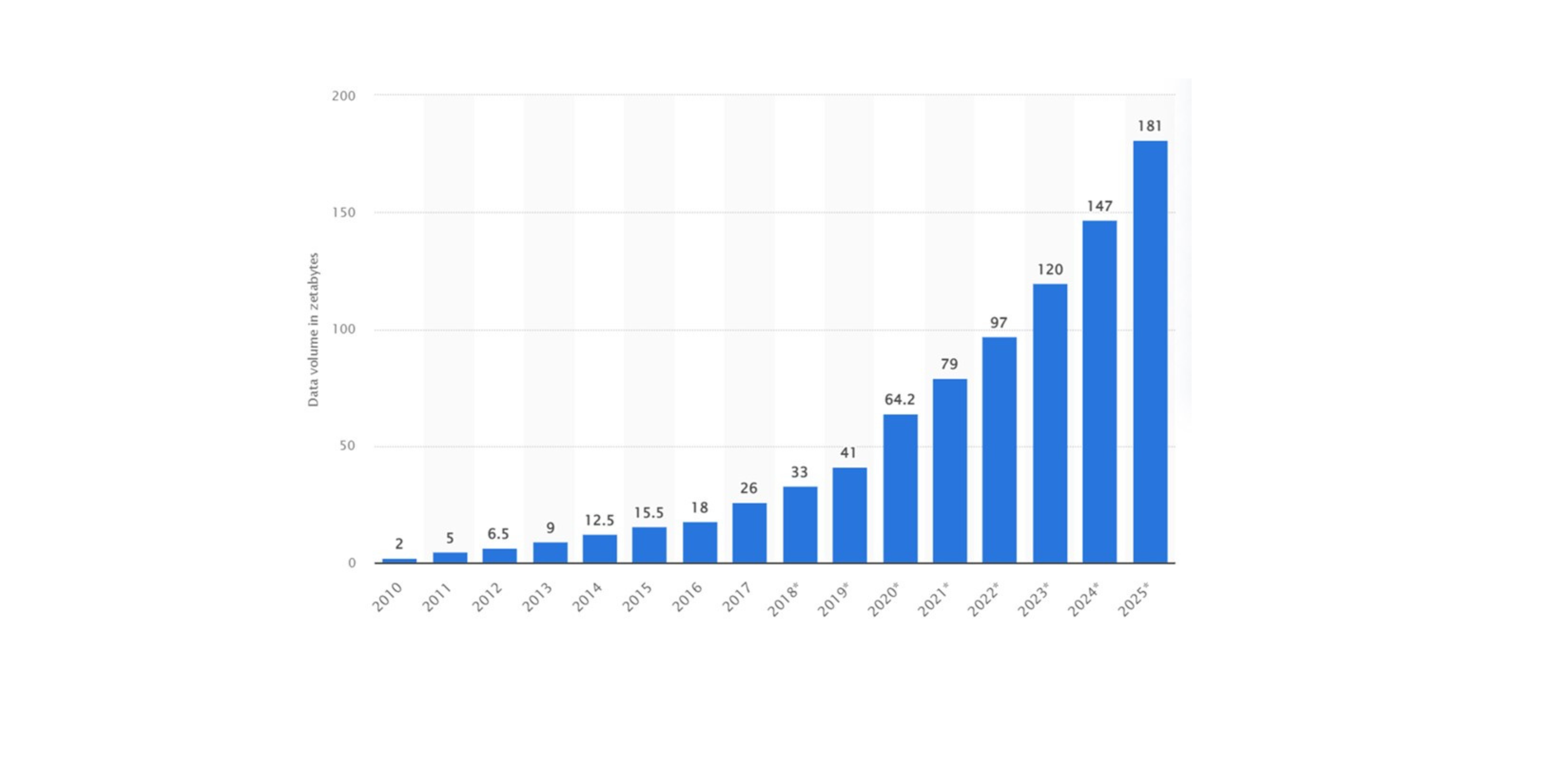
Source: Statista
The above chart depicts data collected worldwide in zettabytes (ZB) as of 2019 and it is estimated by 2025 it would be 181 ZB. A ZB is the equivalent of one trillion gigabytes and a zettabyte is equivalent to about 250 billion full-length movies.
Let's break it down further to understand the mammoth of data collection happening every minute.

Source: eDiscovery Today
What do we do with so much data?
Business Analytics – Need of the hour!
Business Analytics is indispensable in today’s age of big data. It is an optical mix of Data collection, Data Visualization, Data Management, Statistics, Machine Learning, Operations research, and Critical thinking married with Domain Knowledge. An interdisciplinary field that creates insights and values in ways hitherto unheard of in the industry, government, and other fields, thereby providing a competitive advantage.
It refers to the skills, technologies, and practices for continuous iterative exploration and investigation of past business performance to gain insights and drive business planning. Business analytics is a powerful tool in today’s marketplace that can be used to make decisions and craft business strategies.
Across industries, organizations generate vast amounts of data which, in turn, has heightened the need for professionals who are data literate and know how to interpret and analyze that information.
Benefits of business analytics
The potential for data analysis within a business is boundless and without limits. From tracking customer behaviour and input prices to simulating road traffic and competitors’ sales strategies, a skilled Data Scientist can contribute to the success of a business in many ways.
A few of the most crucial advantages of incorporating analytics into businesses are:
a) More Informed Decision-Making
In approaching critical strategic decisions, business analytics can prove to be a valuable asset. When ride-hailing company Uber upgraded its Customer Obsession Ticket Assistant (COTA) in early 2018—a tool that uses machine learning and natural language processing to help agents enhance the speed and precision in addressing support tickets by utilizing prescriptive analytics to determine the effectiveness of the new iteration of the product compared to its original version.
Through A/B testing—a method of comparing the outcomes of two different choices—the company determined that the updated product led to faster service, more accurate resolution recommendations, and higher customer satisfaction scores. These insights not only streamlined Uber’s ticket resolution process but saved the company millions of dollars.
b) Greater Revenue
Firms that adopt data and analytics programs can realize substantial financial gains. According to McKinsey's research, companies that invest in big data achieve a 6% average profit increase, with a jump to 9% for investments lasting five years.
Echoing this trend, a recent study by BARC found that businesses are able to quantify their gains from analyzing data and report an average 8% increase in revenues and a 10% reduction in costs. These results demonstrate the tangible financial rewards that can stem from a well-thought-out business analysis plan - a strategy that many companies can gain an advantage from, as the big data and analytics industry expands.
c) Improved Operational Efficiency
Analytics can serve purposes beyond just financial benefits. It's been discovered that companies are using predictive analytics to optimize their business processes and operations.
According to a KPMG report, organizations use data analytics to identify potential issues before they escalate. For instance, a mobile network provider surveyed in the report stated that they use analytics to predict outages a week before they occur. This enables the company to plan maintenance more efficiently, leading to cost savings and ensuring optimal performance levels of their assets.
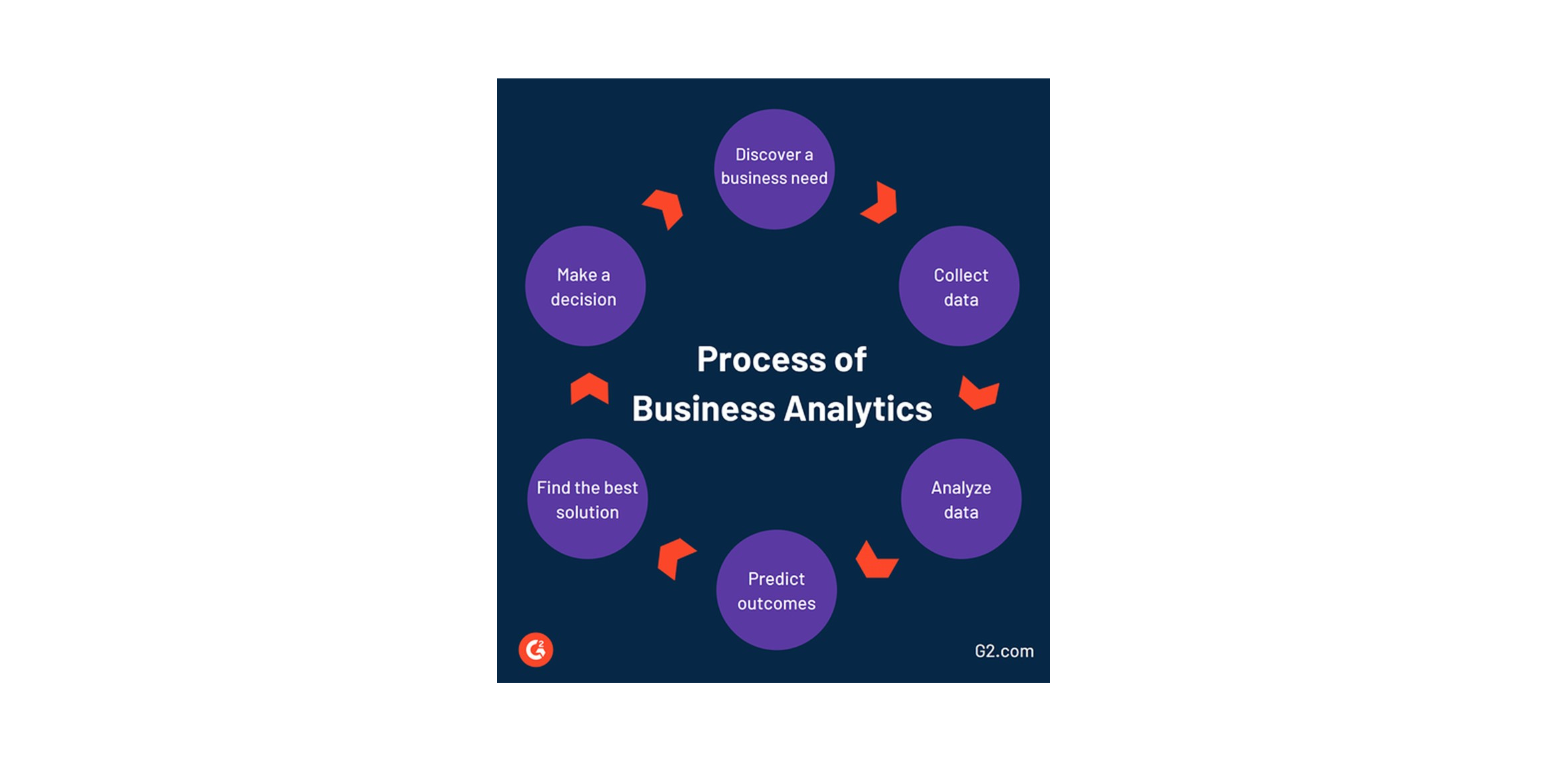
Source: G2
Business analytics is always a recurring and iterative process and sometimes it doesn’t follow any specific cycle as most of the steps need to be visited as required on the job.
Discover a business need:
Identifying a problem statement and understanding the problem would be the most essential aspect of getting to business analytics. Without understanding the business or domain it is practically difficult to get to a solution or apply analytics. This would involve a lot of interaction with the business with an inquisitive and critical-thinking mindset.
This would be the foundational goal of any business analytics solution and getting under the skin of business is quintessential for successful analytics. Any misunderstanding or incorrect information gained from business can lead to a huge blunder or a type 2 error in your hypotheses, leading to a catastrophic impact on your business.
a) Collect data:
After understanding the problem statement or business need and assuming it's done well, you will need to identify sources from where the data can be collected. This would require a holistic approach. Now one must remember that information or data always cannot be made available in a structured or tabular way which is usually a stereotype of how data is expected or perceived.
Data can be in several forms and sizes. For example, for all call centers business data could be of voice or audio-related information, for security agencies image or video data would be necessary, or to understand your end customer perception of your brand social media data (text data) would be needed.
As seen above, in a minute you can have millions of transactions happening all over the globe and sometimes you could be dealing with Terabytes of data to solve a basic problem. Currently, there are various mechanisms and sophisticated infrastructures in place to deal with such mammoth data which is a different discipline in data management.
b) Data preparation:
As mentioned above data comes in varied forms and sizes and much of the data would be in unstructured or sometimes unrecognizable form. It is very important to make sense of the data before we proceed to work on them, hence data preparation is the most important and the hardest part of the entire process which in today’s day and age is the most underrated process when it comes to business analytics or data science for that matter.
Since we are dealing with high volumes of data much of it would be noise and irrelevant to the requirement. With the right domain or business knowledge, it is key to identify the junk which involves the process of data cleaning, transformations, and structuring it out to make better sense of it. A well-prepared data problem is half solved.
c) Analyze data:
Assuming you have prepared the data well, it's important to determine what the data is conveying or the story from the data. Data preparation and Data analysis go hand in hand and are iterative to ensure we have the right information for the problem we are solving. A standard term and technique used to understand data is EDA – Exploratory data analysis.
This helps understand types, distribution (a statistical technique), relationships of variables with one another, and certain useful knowns and unknowns of the business or domain. Proper data analysis helps to identify the key variables or features needed to solve a business problem and most of the time a proper EDA can help solve critical business problems.
d) Predict outcomes:
With robust data analysis and understanding of the variables of a dataset, usually, we can intuitively determine how a certain outcome is achievable or what key factors influence an expected result in the interest of the business either to sustain or grow the business in a broader sense. Therefore, in companies that have a business analytics vertical a lot of emphasis is given, and best practices are put in place for establishing CoE – Center of Excellence to ensure the above points are done well with a set quality output.
But in most cases, we can’t leave it to intuitiveness and assumptions as a business would need scientific backing. Here is where the concepts of advanced statistics come into play to provide us with precision and optimized error results with scientific validation of the outcome.
Further, with a need for a robust solution and scalability, it is essential to employ algorithms (Statistical & Machine learning) that not only help us predict the outcomes with a healthy lead time but also precisely indicate what needs to be done with optimized efforts to achieve them as well.
e) Find the best solution:
The use of algorithms to get precise outcomes is essential for the business which reduces the risk of uncertainty and helps plan better. But there are several algorithms to solve basic problems. It is a good practice in business analytics to be iterative with the use of the right algorithms and varying factors (simulate worst to best-case scenarios) to arrive at varied outcomes and choose the best or optimal outcomes depending on the business requirement. This would further strengthen your case for the solution you will provide to the business.
f) Make a decision:
As seen through the above points, business analytics is a key enabler to make the right decisions with various methods and techniques. It has a proven record and sophisticated scientific backing which simulates real-world scenarios and helps us understand the best decisions in order to achieve the business goals or needs.
Essentials of Business Analytics:
Business analytics has many use cases, but when it comes to commercial organizations, Business Analytics is typically used to:
- Analyse data from a variety of sources. This could be anything from cloud applications to marketing automation tools and CRM software.
- Use advanced analytics and statistics to find patterns within datasets. These patterns can help you predict trends in the future and access new insights about the consumer and their behaviour.
- Monitor KPIs and trends as they change in real-time. The ability to centralize business data and swiftly arrive at precise conclusions is made attainable with this feature.
- Support decisions based on the most current information. With business analytics providing such a vast amount of data that you can use to back up your decisions, you can be sure that you are fully informed for not one, but several different scenarios.
While these are the most common use cases, there are four primary methods of business analysis. They’re implemented in stages, starting with the simplest. One method isn’t more important than another, it all depends on what your end goal is when using Business Analytics.
4 Primary Techniques of Business Analysis
The four primary techniques of business analysis, widely employed, are executed in a step-by-step manner starting with the least complex one. The significance of each method varies depending on the intended outcome of using Business Analytics.
By implementing these four types of analysis, your data undergoes a thorough process of cleansing, examination, and comprehension, enabling you to craft solutions to any obstacle your organization might encounter.
- Descriptive Analytics: Analyzing historical data and key performance indicators to uncover trends and patterns through interpretation. This allows for looking at the larger picture view of what happened in the past and what is happening currently using data aggregation and data mining techniques. Many companies use descriptive analytics for a deeper look into the behaviour of customers and how they can target marketing strategies for those customers.
- Diagnostic Analytics: Examining past performance to identify the factors that shape particular trends is the central focus of this process. This is accomplished by utilizing drill-down, data discovery, data mining, and correlation analysis to uncover the root causes of specific events. Once a comprehension of the probability of the event and the reasons behind it is established, algorithms for classification and regression are applied.
- Predictive Analytics: Uses statistics to forecast and assess future outcomes using statistical models and machine learning techniques. This often takes the results of descriptive analytics to create models that determine the likelihood of specific outcomes. This type of analytics is often used by sales and marketing teams to forecast the opinions of specific customers based on social media data.
- Prescriptive Analytics: Draws upon historical performance information to suggest the best approach for comparable circumstances in the future. Not only does this type of business analytics determine outcomes, but it can also recommend the specific actions that need to occur to have the best possible result. This is often achieved using deep learning and complex neural networks.
This type of business analytics is often used to match various options to the real-time needs of a consumer. Deciding which method to go with will depend on the business situation at hand.
Prerequisite for Business Analytics:
a) Domain knowledge or Business Understanding:
Understanding the domain or business is very essential without which you cannot be successful in the implementation of analytical solutions. Without domain or business understanding the business teams will never take you seriously and they will result in cut down or no analytical projects coming your way.
b) Disciplinary of Science:
In order to come up with scientific explanations of outcomes to enable decisions, it is important to have a good understanding of certain disciplines of science majorly mathematics and statistics. In order to understand the right applications of algorithms on a given data set, it is necessary to align the outcomes of the algorithm with the business need.
c) Computer application and programming language:
In order to handle large data sets and application of mathematical or statics to the data, to do it manually on a piece of paper or in a spreadsheet is going to take a lifetime. Hence, computer applications and program language help achieve this process in speed enabling quick turnaround and results for the business with healthy lead time. This helps to mitigate the business risk in advance and have ample time to come out with the best decisions.
d) Analytical thinking:
Having all the above prerequisites will help you only to perform your task in a robotic or mundane manner. Analytical thinking is essential to look at a problem with varied perspectives and come up with innovative and best possible ways to solve a problem using data.
Challenges of Business Analytics:
A vast amount of data is created daily, presenting businesses with never-ending data analysis challenges. For instance, Statista foresees a steady rise in the amount of data generated, reaching 90 zettabytes by 2022 and doubling in size by 2025.
Data analytics plays a crucial role in helping companies make informed decisions, increase efficiency, and gain a competitive edge. But in the face of the fast-growing volume of data, and the apparent challenges (storing, managing, analyzing), achieving these goals can be an uphill task.
For these reasons, businesses (more so analysts) must be well-versed in possible data analysis challenges to find appropriate ways to navigate them and gather the appropriate insights to inform business decisions and processes.
We delve below into several frequent difficulties encountered by data analysts in their analysis and outline the methods they use to overcome them.
Managing vast amounts of data
A copious amount of daily gathered data can quickly turn into a chaotic jumble without a streamlined automated data management solution in place. Look at it this way. Data is created for every interaction across your channels – email, social, website, paid search ads, and virtual store. With time, analyzing it can get overwhelming, hindering the insights’ completeness.
Yet, it remains essential to leverage the data to extract meaningful insights that can drive business growth and help maintain a competitive advantage. Thus, to avoid time-consuming and inefficient procedures, not forgetting the high risk of inaccuracy, it’s essential to use analytics tools to collect, manage, and analyze the data in real-time.
i. Collecting meaningful data
With the high volume of data available for businesses, collecting meaningful data is a big challenge. Ideally, employees spend much time sifting through the data to gain insights, which can be overwhelming. Besides, it’s impossible to sort and analyze all the data in real time, which might fail to provide accurate and relevant reports.
An appropriate data analytics tool can effortlessly assist you in conquering this issue. The tool can help you collect, analyze, and provide real-time reports for better decision-making. On the same note, it reduces the time employees spend collecting and analyzing data, thereby boosting productivity.
To maximize the benefits of data analytics tools, a well-rounded approach would be to couple their usage with employee education on proper data utilization, be it through online courses or in-person training sessions.
ii. Selecting the right analytics tool
An inadequate tool for your business's data analytics needs can impede efficient and accurate data analysis. Different analytics tools (Power BI, Tableau, RapidMiner, etc.) are available and offer varying capabilities. While taking into account your budget, additional factors such as alignment with your business goals, scalability, integration potential, and the capability to gather insights from multiple data sources should also be considered when choosing a data analytics solution.
A skilled data analyst should possess the expertise to determine the appropriate tool for the job. But since the analytics landscape is changing quickly, those not conversant with modern data analytics could enroll in a refresher course to hone their skills. As an alternative, seeking advice from a professional can provide valuable insight into selecting the most fitting tool for your business requirements.
iii. Data visualization
Data must be presented in a manner that promotes clarity and comprehensiveness. Usually, this is in the form of graphs, charts, infographics, and other visuals. Unfortunately, doing this manually, especially with extensive data, is tedious and impractical. For instance, analysts must first sift through the data to collect meaningful insights, then plug the data into formulas and represent it in charts and graphs.
The process can be time-consuming, not forgetting that the data collected might not be all-inclusive or real-time. But with appropriate visualization, this becomes much easier, more accurate, and relevant for prompt decision-making.
iv. Data from multiple sources
Usually, data comes from multiple sources. For instance, your website, social media, email, etc., all collect data you need to consolidate when doing the analysis. However, doing this manually can be time-consuming. You might not be able to get comprehensive insights if the data size is too large to be analyzed accurately.
Software built to collect data from multiple sources is reliable. It accumulates all essential information for examination and generates comprehensive reports with a reduced chance of inaccuracies.
v. Low-Quality Data
Inconsistent information presents a significant obstacle in conducting data analysis. Generally, manual data entry is prone to errors, which distort reports and influences bad decisions. Also, manual system updates threaten errors, e.g., if you update one system and forget to make corresponding changes on the other.
Fortunately, having the tools to automate the data collection process eliminates the risk of errors, guaranteeing data integrity. Moreover, software that supports integrations with different solutions helps enhance data quality by removing asymmetric data.
vi. Data Analysis skills challenges
A shortage of experts with analytical expertise poses another formidable challenge for businesses. The lack of proficiency in comprehending diverse datasets may restrict the number of insights that can be gleaned from data analysis.
In addition to hiring talent with data analysis skills, you should consider acquiring easy-to-use and understanding software. Alternatively, you could conduct training programs to equip employees with the most up-to-date data analysis skills, especially those handling data.
vii. Scaling challenges
With the rapidly increasing data volume, businesses face the challenge of scaling data analysis. The accumulation of data makes it increasingly challenging to analyze and produce insightful reports. This becomes even more cumbersome when relying on analytics software, especially if the technology lacks scalability.
That’s why it’s important to consult before acquiring a tool to ensure it’s scalable and supports efficient data analysis as your business grows.
viii. Data security
Data security is another challenge that increases as the volume of data stored increases. Businesses must enhance their security protocols to decrease the likelihood of potential breaches to the greatest extent feasible.
There are several ways of mitigating the risks, including controlling access rights, encrypting data with secured login credentials, and conducting training on big data. Alternatively, you could hire cybersecurity professionals to help you monitor your systems.
ix. Budget limitations
Data analysis is a cost-intensive process. It can be a costly investment, from acquiring the right tools to hiring skilled professionals and training the employees on the basics of data analysis. Again, with the high volatility of data, managers must be proactive to secure the system and address any security threats while scaling the system to accommodate the growing volume of data.
While it's desirable for risk management to be a streamlined process for small businesses, securing funding to implement risk management strategies can be difficult. Nevertheless, obtaining the right tools and acquiring the necessary expertise to utilize data analysis is a must. Hence, decision-makers must be discerning in their choice of solutions and present thorough return on investment (ROI) projections to validate budget requirements.
x. Lack of a data culture
A company's organizational culture plays a crucial role in determining the success of its data analysis efforts. According to a study on business intelligence, 60% of businesses surveyed cited company culture as their most significant challenge. However, most companies are not data-driven and have not equipped their employees with the necessary knowledge of data analysis.
To overcome this challenge, it’s crucial to equip your employees to support data culture by providing the necessary training.
xi. Data inaccessibility
Data collected can only benefit the business if it is accessible to the right people. From the analysts to the decision-makers, businesses need to make sure every key person has the right to access the data in real-time and be fully empowered with knowledge on how to analyze different data sets and use the insights.
Mainly, businesses restrict system access for security reasons. But with appropriate security safeguards, you can enhance safer and unrestricted data access for analysis and decision-making purposes.
xii. Translating Business Analytics to business teams:
After investing a lot of effort in the business analytics processes and getting the right results which are decision enablers to the business. A very important and underrated challenge is conveying the results to the business teams. One must understand that the business is not equipped with technical skills which enable business analytics and hence conveying or convincing the business teams of the results (even though scientifically proven) is a hard job.
Most of their decisions are intuitive and driven by gut and the result of business analytics can be counterintuitive and sometimes challenging to their experience, which can lead to a decline to consume the results from business teams.
To overcome this, it is essential to speak the business language and storyboard the results in a way it is understood by the business with apt and simple visualization and with crisp explanations.
Conclusion
With the vast amount of data created daily, businesses face the huge challenge of sifting through all the various data sets to draw valuable insights to make informed business decisions. Besides the possibility of messy data due to the high volume, they also face other challenges such as collecting meaningful data, selecting the right analytics tool, data visualization, multiple-source data, low-quality data, lack of skills, scaling challenges, data security, budget limitations, lack of a data culture, and inaccessibility.
Fortunately, they can overcome these challenges by investing in a suitable data analytics tool, training employees on data analysis, and stepping up their cybersecurity safeguards, among other suggested solutions.
Business analytics is still in its infant stages with many established organizations. With the digital revolution in recent times, organizations are understanding the importance of business analytics practices and realizing the impact of using business analytics to run or sustain their businesses.
It is a growing field and there are a lot of communities created that contribute on a daily basis in bringing out innovative ways to simplify and achieve business goals for better consumption of this practice.













